What causes nail fungus?
Nail fungus develops when fungi invade the nail plate or nail bed, typically through tiny breaks in the nail or surrounding skin. The most common culprits are dermatophytes, the same group of fungi responsible for athlete’s foot, though yeasts and moulds can also cause infection.
Key contributing factors include:
- Warm, moist environments — enclosed shoes and sweaty feet provide an ideal breeding ground for fungi.
- Poor foot hygiene — infrequently changing socks or shoes allows fungal spores to multiply.
- Existing skin infections — untreated athlete’s foot can easily spread to the toenails.
- Nail trauma — injury or damage creates small openings where fungi can enter.
- Health and age factors — older adults and individuals with diabetes, poor circulation or weakened immunity are more susceptible.
Without proper treatment, the infection may persist or spread, making nails progressively thicker, brittle and harder to manage.
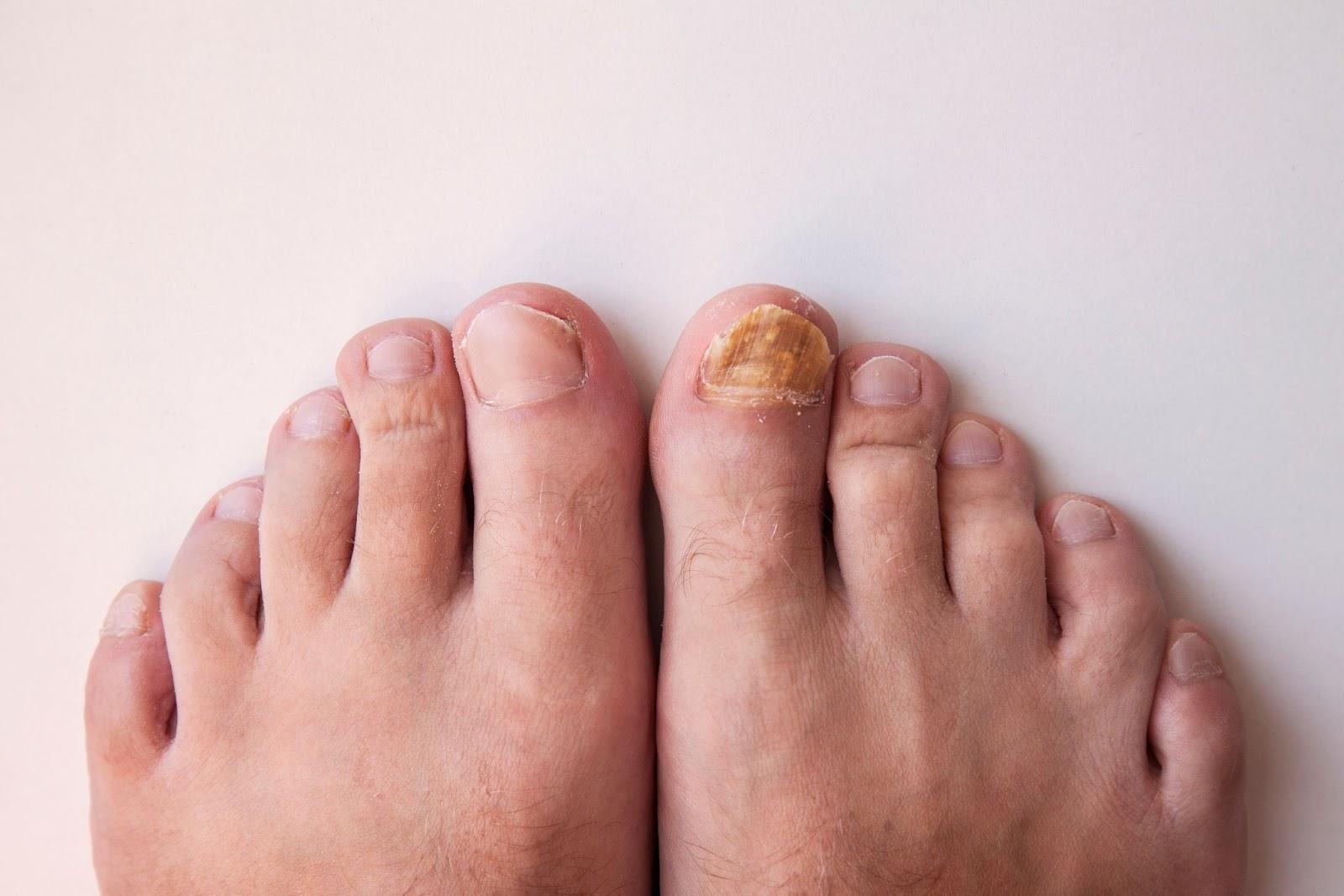
What does nail fungus look like?
In its early stage, nail fungus often begins as a faint white or yellow spot near the nail tip. As the infection spreads, the nail thickens and discolours, turning yellow, brown, green or even black. The nail may become rough, brittle and crumbly, and in advanced cases, separates from the nail bed (onycholysis)
Other signs include:
- Distorted nail shape or irregular growth
- Chalky debris beneath the nail
- Mild odour or discomfort in footwear
- Dry, flaky or scaly skin around the affected toe
When several nails become affected, nail care and walking may become difficult and painful. Early diagnosis makes treatment easier and prevents progression.
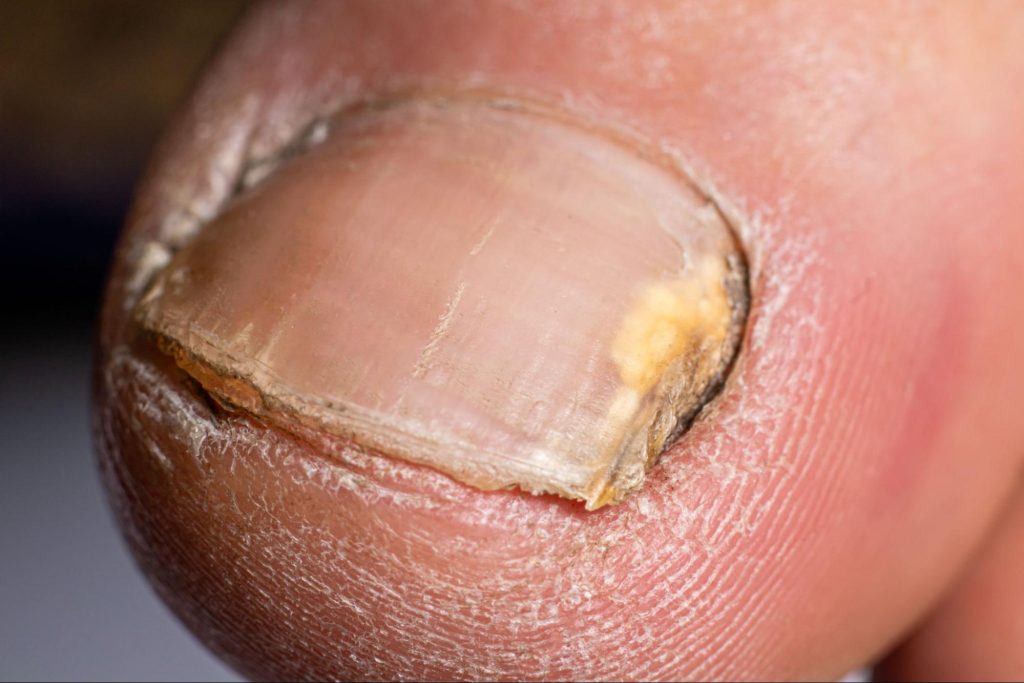
What are the symptoms of nail fungus?
Nail fungus often develops slowly, and symptoms can vary depending on the type and severity of the infection. In the early stages, you may notice slight discolouration or thickening of one nail, which can gradually spread to others if left untreated.
Common signs of nail fungus include:
- Yellow, green, brown or white discolouration of the nail
- Thickened or brittle nail texture
- Rough, crumbly or flaky nail edges
- Nail separating from the nail bed (onycholysis)
- Changes in nail shape or uneven growth
- Pain, tenderness or discomfort when pressure is applied
- A foul odour coming from the affected nail
In advanced cases, the infected nail may become distorted and cause discomfort when walking, wearing shoes or trimming the nail. The surrounding skin might appear dry or scaly, especially if athlete’s foot is also present.
Recognising these symptoms early helps prevent the infection from spreading and allows for more effective treatment.
Complications of nail fungus
Untreated nail fungus can progress and cause:
- Persistent thickening, brittleness and discolouration
- Nail detachment or deformity
- Secondary bacterial infection in the surrounding skin
- Pain and difficulty walking or wearing shoes
- Spread of infection to other nails or skin
- Slow healing in individuals with diabetes or vascular disease
Chronic infections may result in permanent nail deformity or total nail loss. Early professional care prevents these complications and restores healthy nail growth.
How is nail fungus diagnosed?
Nail fungus can resemble other nail conditions, so an accurate assessment by a medical professional is important to confirm infection and prevent unnecessary or ineffective treatment.
- Clinical examination — the podiatrist inspects the nail for signs such as thickening, brittleness and colour change.
- Medical history — questions about symptoms, lifestyle and health conditions (e.g. diabetes or poor circulation).
- Laboratory testing — the podiatrist may refer patients to do nail sample testing (e.g. microscopy or culture) to identify the presence of fungi.
- Severity assessment — determines how deeply the infection has penetrated and whether multiple nails are involved.
Accurate diagnosis ensures that treatment is targeted and effective, which helps avoid unnecessary or incorrect therapy.
How is nail fungus treated?
The right treatment for nail fungus depends on the severity of the infection, the number of nails affected, and whether the nail matrix (growth area) is involved.
Early, targeted management helps clear the infection, restore nail health, and prevent recurrence.
- Topical antifungal medication: medicated creams or nail lacquers are suitable for mild infections and work best when used consistently for several months.
- Debridement and nail trimming: a podiatrist can thin and trim thickened nails to reduce pressure and help medication penetrate better.
- Lunula laser (cold laser therapy): this non-invasive, pain-free treatment uses dual-wavelength low-level laser light to promote healing, improve nail health, and assist the body in eliminating fungal pathogens. It is chemical-free and may reduce the risk of recurrence.
- Partial or total nail removal: in advanced or recurrent cases, removing part or all of the affected nail under local anaesthetic allows direct treatment of the nail bed and encourages healthy regrowth.
- Oral antifungal medication: for moderate to severe infections, a podiatrist may refer for prescription tablets to clear the infection more effectively.
Professional evaluation is important to determine the most suitable approach for your condition. Combining medical treatment with proper foot hygiene and lifestyle changes provides the best long-term results.
Prevention tips for nail fungus
Simple daily habits can significantly lower the risk of fungal infection and recurrence:
- Maintain good foot hygiene — wash and dry your feet thoroughly, especially between the toes.
- Wear breathable footwear — choose shoes that fit comfortably and allow ventilation; avoid prolonged use of enclosed shoes.
- Change socks daily — opt for moisture-wicking fabrics like merino wool, polyester and nylon.
- Avoid walking barefoot in communal areas — use slippers in gyms, pools and public showers.
- Do not share footwear or nail tools — this prevents fungal transmission.
- Treat skin infections early — manage athlete’s foot promptly to prevent spread to the nails.
Regular podiatric check-ups and foot care can help detect early signs before the infection worsens.
Summary
Nail fungus (onychomycosis) is a common toenail infection caused by fungi that thrive in warm, moist environments. It leads to thickened, brittle and discoloured nails that may separate from the nail bed over time. Though not life-threatening, the condition can be stubborn and cause pain or difficulty walking.
Diagnosis typically involves history taking and clinical examination. Podiatric treatments may include topical antifungal medication, debridement, laser therapy or nail removal for severe cases. Preventive habits such as proper foot hygiene, breathable footwear and early treatment of minor infections can greatly reduce recurrence.
If you notice persistent nail discolouration, thickening, or brittleness, schedule a consultation with Atlas Podiatry for an evaluation and effective treatment to restore nail health and comfort.