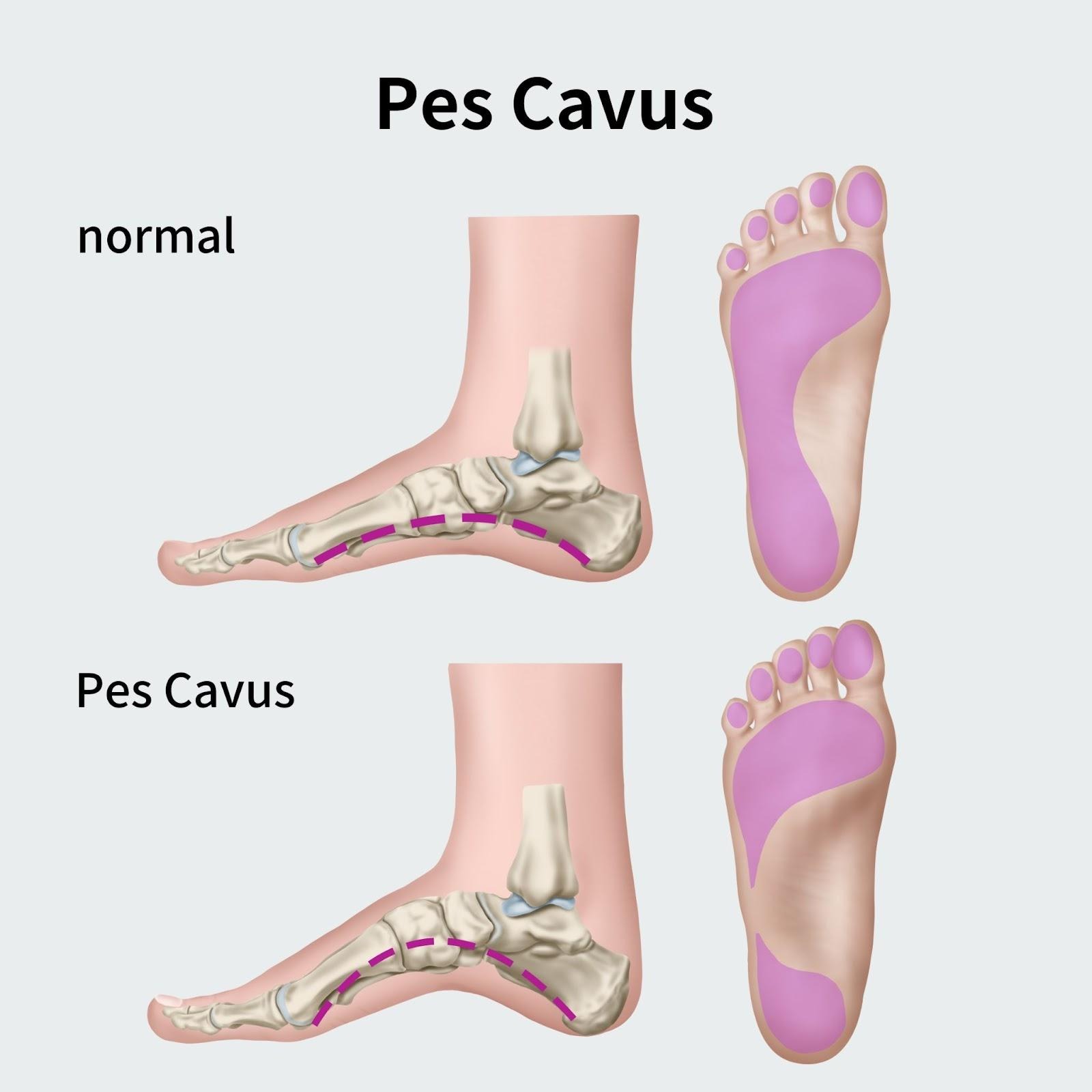
What causes high arch feet?
High arch feet can develop due to a range of factors that affect how the muscles and nerves control foot movement. Identifying the cause is important, as it helps guide appropriate management and prevent complications.
Common causes of high arch feet include:
- Neurological conditions that affect muscle control and foot positioning
- Muscle imbalance where certain muscles overpower others, raising the arch
- Inherited foot structure, passed down through family members
- Idiopathic causes, where no clear underlying reason is identified
A professional assessment helps determine the likely cause and the most suitable treatment approach.
How can high arch feet affect the feet and lower limbs?
High arch feet can significantly alter how pressure is distributed across the foot during standing and walking. Because the arch remains rigid and does not flatten normally, more weight is concentrated on the heel and the ball of the foot, increasing the risk of pain and pressure-related problems.
Reduced shock absorption means impact forces are less effectively cushioned and are transmitted through the foot and up the lower limbs. Over time, this can place additional strain on the ankles, knees, hips and surrounding soft tissues. As a result, individuals with high arches may be more prone to joint pain, instability and repetitive strain injuries.
Without proper support, high arch feet can also increase stress on tendons and ligaments, contributing to fatigue, discomfort and a higher risk of injury during daily activities or exercise.
What are the symptoms of high arch feet?
High arch feet can lead to a range of symptoms due to uneven pressure distribution and reduced shock absorption during movement. Symptoms may vary in severity and often worsen with prolonged standing or activity.
Common symptoms of high arch feet include:
- Foot pain or instability, particularly during walking or exercise
- Calluses and pressure points under the heel or forefoot
- Recurrent ankle sprains due to reduced stability
- Heel pain, especially after activity
- Toe deformities, such as claw toes or hammer toes

Which foot and ankle problems are commonly associated with high arches?
High arches can increase the risk of several foot and ankle conditions by placing excess stress on specific areas of the foot.
Commonly associated conditions include:
- Plantar fasciitis
- Ankle instability
- Metatarsalgia (pain in the ball of the foot)
- Stress fractures, particularly in the forefoot
Early assessment helps identify these issues and reduce the risk of long-term complications.
How are high arch feet diagnosed?
At Atlas Podiatry, high arch feet are diagnosed through a detailed clinical assessment by our podiatrist. This includes examining foot structure, joint movement and areas of pressure, as well as observing how the feet function during standing and walking.
Assessment may involve:
- Gait analysis to evaluate walking patterns and load distribution
- Neurological screening where an underlying nerve or muscle condition is suspected
- Recommendations for imaging, such as X-rays, when further evaluation of structural changes or associated injuries is needed
Accurate diagnosis helps guide appropriate treatment and long-term management.
When should high arch feet be assessed by a podiatrist?
High arch feet should be assessed when they begin to cause symptoms or interfere with daily activities. Early evaluation can help prevent ongoing discomfort and injury.
Assessment is recommended if you experience:
- Frequent ankle sprains or instability
- Foot or ankle pain
- Painful calluses or pressure points
- Balance difficulties or repeated injuries
How do high arch feet affect gait and lower limb alignment?
High arch feet are commonly associated with supination, where the foot rolls outward during walking. This limits the foot’s ability to absorb shock and adapt to the ground.
Poor shock absorption increases impact forces transmitted through the ankles, knees and hips, placing added strain on these joints. Over time, this altered gait pattern can contribute to joint pain, instability and a higher risk of overuse injuries in the lower limbs.
What treatment options are available for high arch feet?
Treatment for high arch feet focuses on managing symptoms, improving foot function, and reducing the risk of injury. As the foot structure itself cannot usually be changed, management aims to improve shock absorption, redistribute pressure and support stability during daily activities. In most cases, conservative podiatric care is effective in relieving discomfort and preventing further complications.
How can podiatric treatment help manage high arch feet?
At Atlas Podiatry, management of high arch feet is tailored to how your feet function and how symptoms affect your daily life. Treatment is designed to improve comfort, stability and long-term foot health.
Podiatric treatment may include:
- Custom orthotics (insoles) to improve cushioning, redistribute pressure and enhance shock absorption.
- Footwear assessment and recommendations to provide adequate support and reduce impact forces.
- Load redistribution strategies to minimise pressure on high-stress areas of the foot.
- Stability support, such as bracing where required, to reduce ankle instability.
- Injury prevention strategies to lower the risk of sprains, stress fractures and overuse injuries.
By addressing the mechanical demands placed on the feet, podiatric care helps improve function, reduce pain and support safer, more confident movement.
What role does footwear and support play in high arch feet?
Footwear plays an important role in managing high arch feet by compensating for reduced natural shock absorption. Shoes with adequate cushioning, heel support and stable midsoles help absorb impact forces and reduce pressure on the heel and forefoot. Supportive footwear also improves overall stability and comfort during walking and standing.
Minimal or poorly cushioned footwear should generally be avoided, as it can increase impact loading and worsen symptoms. When combined with appropriate support, well-chosen footwear can significantly reduce discomfort and lower the risk of injury.
Can high arch feet be prevented or corrected?
The high arch foot structure cannot always be prevented or permanently corrected conservatively. However, the symptoms and complications associated with high arches can be effectively managed.
With early assessment, appropriate footwear and podiatric support such as custom orthotics, it is possible to reduce pain, improve stability and prevent long-term problems related to high arch feet.
Summary
High arch feet, also known as pes cavus, can affect how the feet absorb shock and distribute pressure, often leading to pain, instability and a higher risk of injury in the feet and lower limbs. Without proper support, high arches may contribute to calluses, ankle sprains, joint strain and ongoing discomfort during daily activities.
Assessment by a podiatrist helps identify how foot structure and gait patterns are contributing to symptoms and guides effective, conservative management. At Atlas Podiatry, care focuses on improving comfort and stability through custom orthotics, footwear advice and injury prevention strategies tailored to individual needs.
If you are experiencing pain, instability or recurrent injuries related to high arch feet, schedule a consultation with Atlas Podiatry for a comprehensive assessment and personalised treatment plan to support long-term foot health and confident movement.